Optimise Patient Access
The carefully created courses are designed to help you deliver the best possible experience for staff and patients.
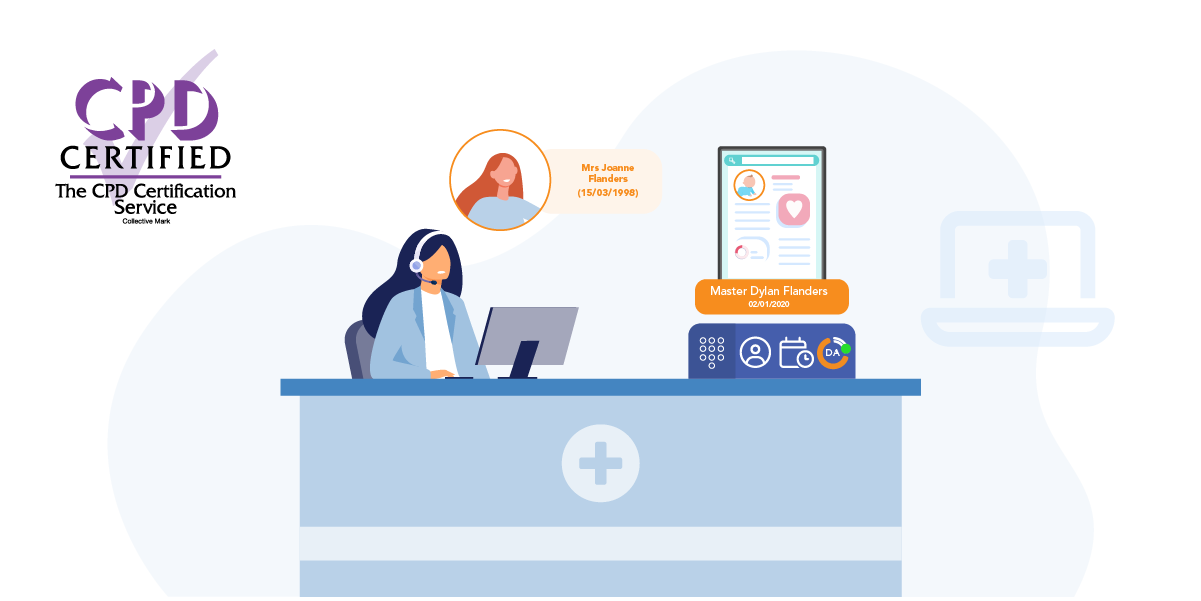
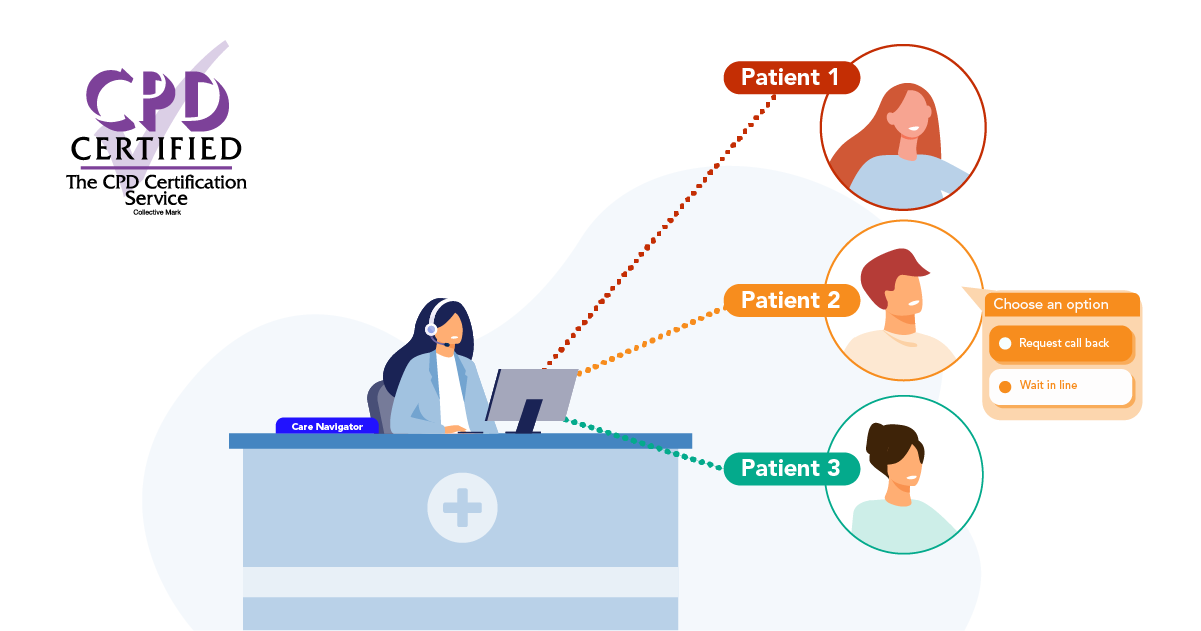
In primary care, delivering a great patient experience is more critical than ever. To deliver modern general practice successfully surgeries not only need to have the right tools in place, but they need to know how to utilise those tools effectively.
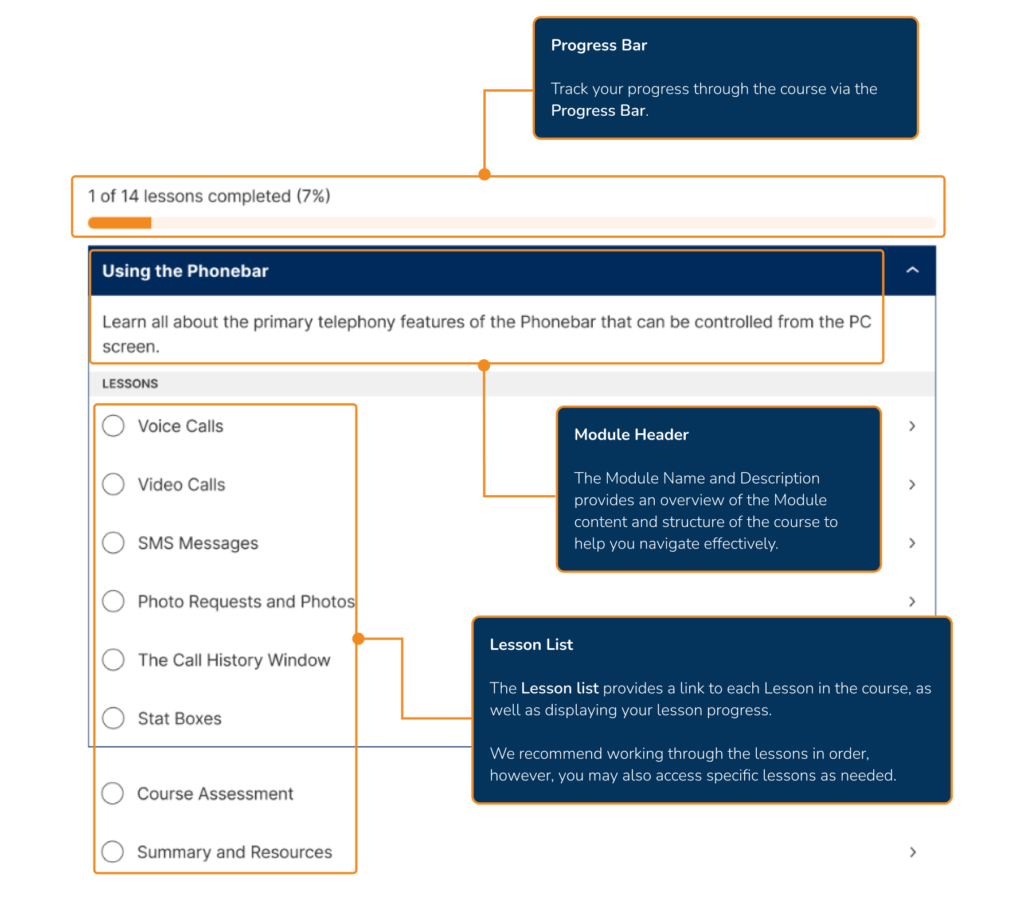
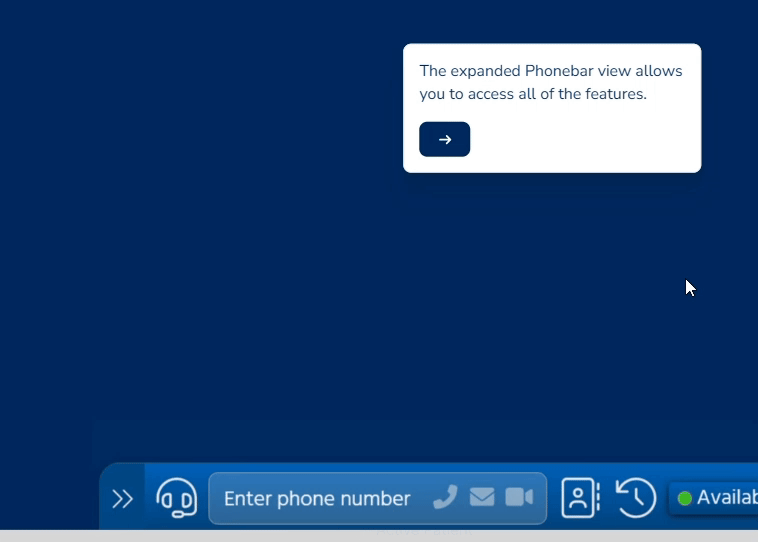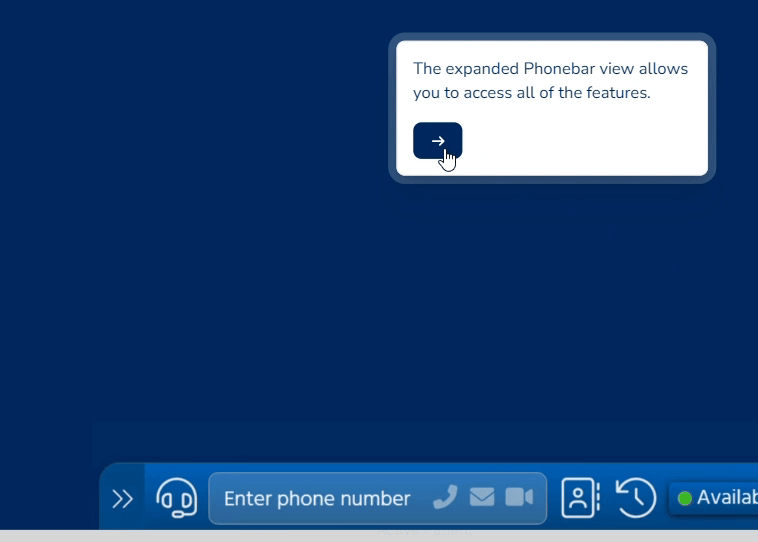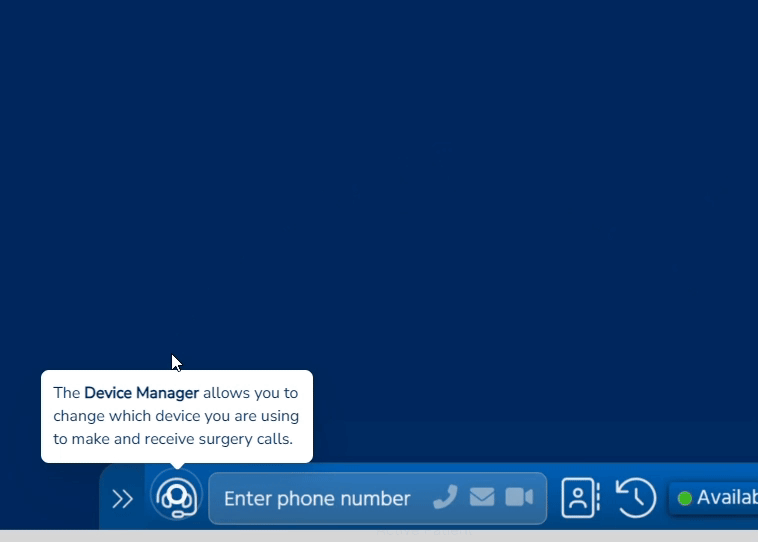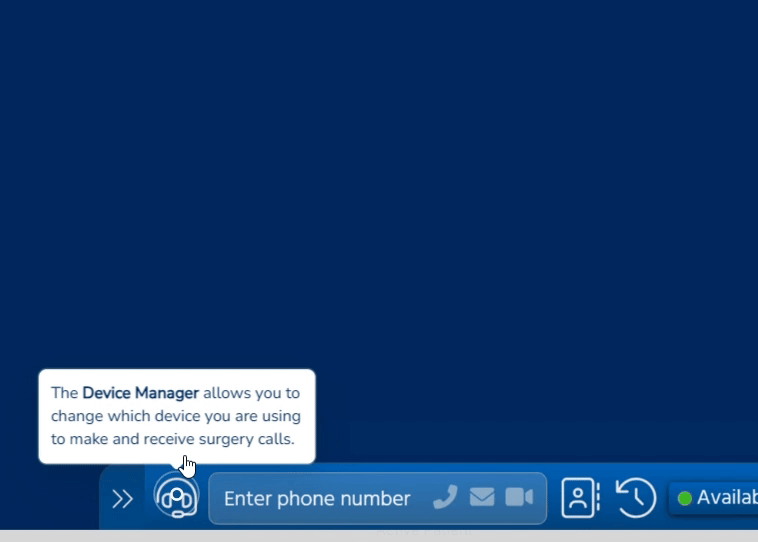
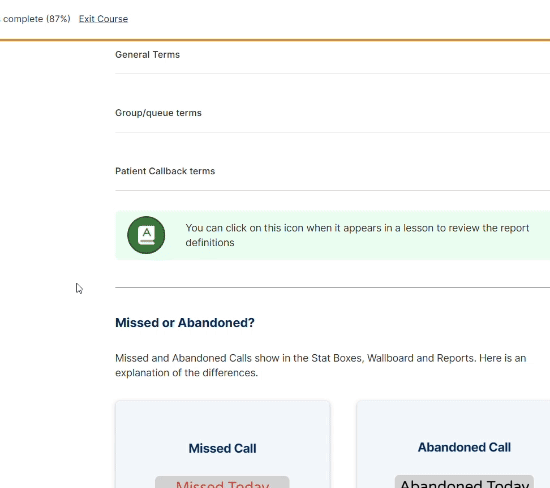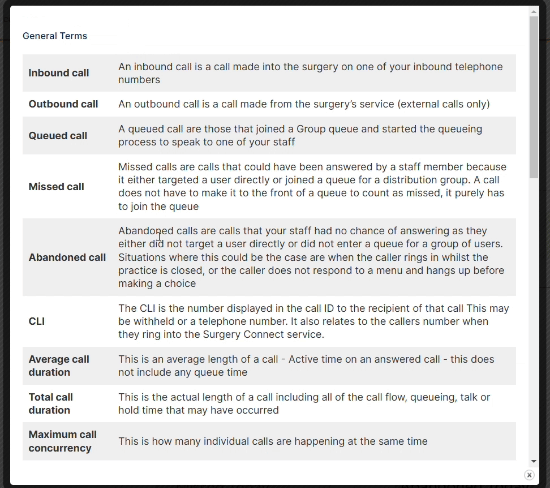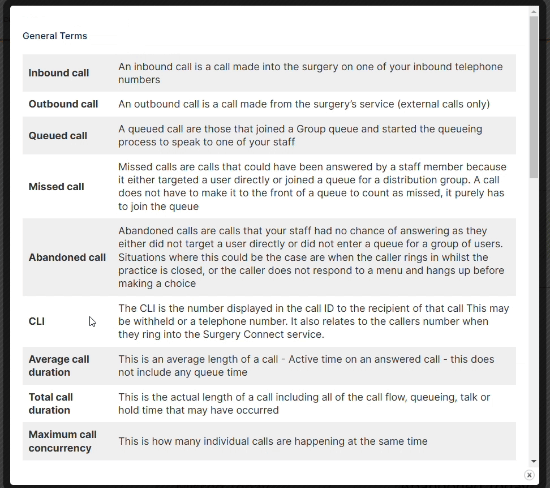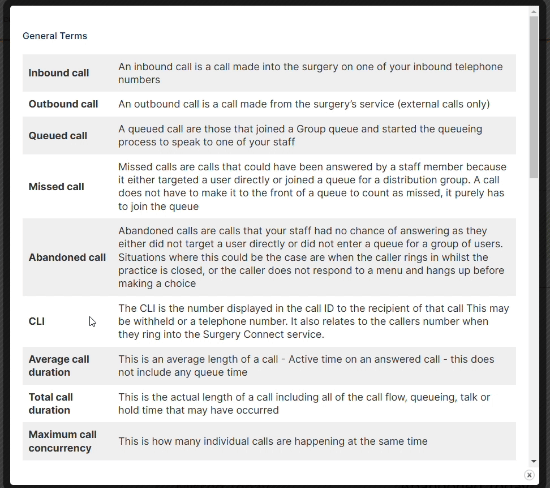
Access Optimisation supports practices to get the most out of digital telephony, through the many features of Surgery Connect. These interactive eLearning courses will help you do just that.
Access Optimisation Courses
X-on Health has collaborated with practices to hone Surgery Connect. We have created bespoke training courses to help you maximise the benefits of our features.
Access Optimisation National Webinar Series

To help support Access Optimisation, we have created a series of complimentary webinars focusing on the key features at the centre of improved access.
In each episode our experts dive into the benefits of each function and provide with practical insights on leveraging these features to their fullest potential.